Conventional Scanner vs. RKS300: How Thermal Monitoring of Kilns Has Evolved
Controlling the temperature of a rotary kiln is critical in industries such as cement and steel. Effective temperature control reduces risks, prevents damage to the kiln shell, and helps maintain process efficiency. Traditionally, rotary kilns have been monitored using scanners with rotating mirrors, but today more advanced systems such as the RKS300 are available, providing a more complete, reliable, and safer way to monitor the kiln shell.

How Temperature Is Measured
Conventional Scanner
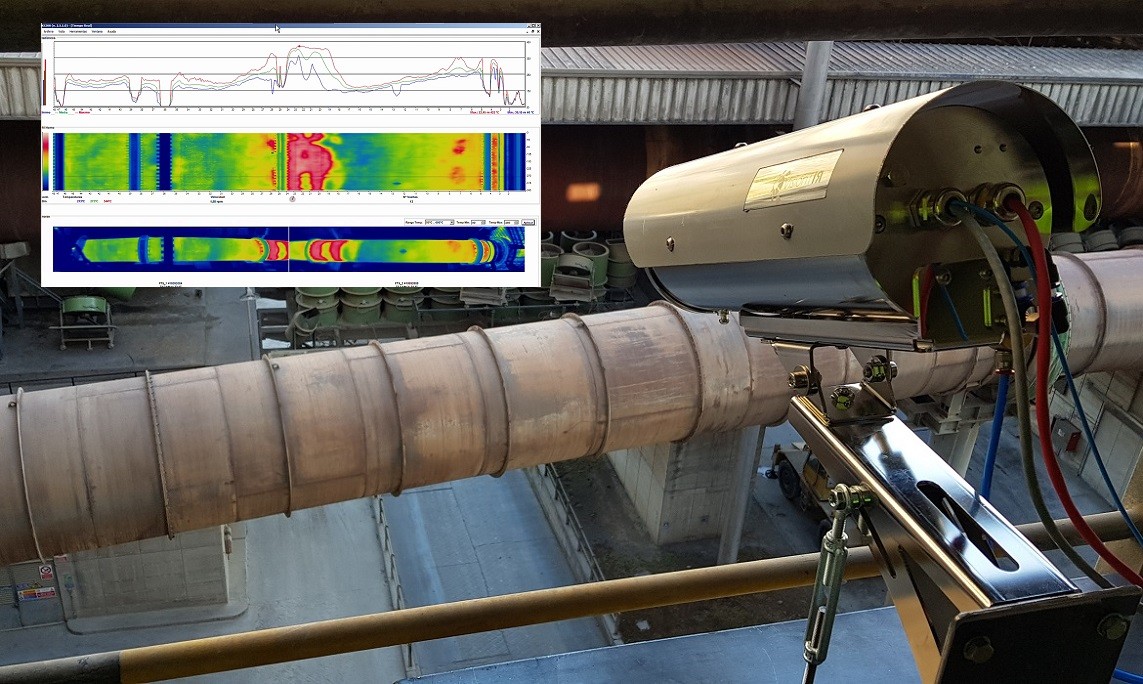
A conventional scanner measures temperature using a rotating mirror, generating a spiral scanning pattern. This means that certain areas of the kiln may not be measured during each cycle, making the early detection of hot spots or thermal anomalies more difficult.
RKS300
The RKS300, by contrast, measures the temperature of the entire kiln surface simultaneously, without leaving any areas unmonitored. This significantly improves the reliability of temperature control and enables faster, more effective detection of thermal anomalies.

Maintenance and Moving Parts
Scanners with rotating mirrors require more maintenance because they rely on components that are in constant motion. This results in regular adjustments, inspections, and a higher likelihood of wear over time.
The RKS300 has no moving parts, which significantly reduces maintenance requirements and makes the system more reliable in the long term, with fewer shutdowns and lower operating costs.

Visualización de los datos
Otra diferencia importante es la visualización. El RKS300 permite ver vídeo termográfico en tiempo real, mostrando con claridad cómo se distribuye la temperatura sobre el horno. Esta visión completa ayuda a identificar patrones térmicos, actuar con rapidez y mejorar la seguridad de operación.
En cambio, los escáneres tradicionales suelen entregar datos punto por punto, sin ofrecer una imagen térmica completa de forma instantánea.
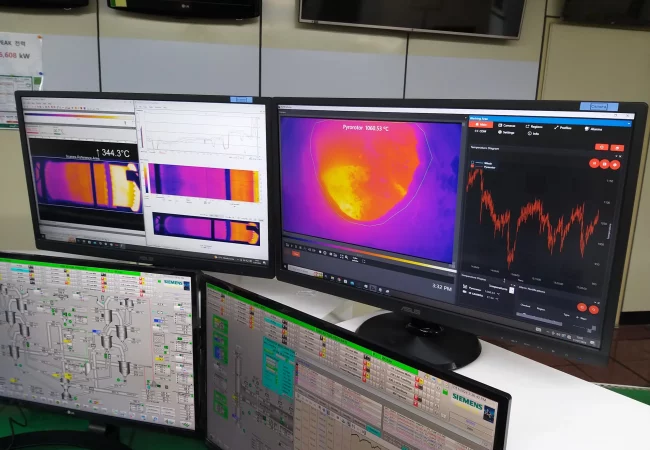
Control room visualization: real-time thermography enabling fast, informed, and safe operational decisions.
Flexibility and Calibration
The RKS300 is a flexible system: additional thermographic cameras or pyrometers can be added to cover any shadowed areas or zones outside the field of view. In addition, the system continuously self-calibrates, adjusting to the actual kiln temperature to maintain measurement accuracy during operation.

Conclusion
Traditional scanners have been useful for many years, but the RKS300 represents a significant step forward: greater coverage, more accurate measurement, reduced maintenance, and a complete real-time thermal view. For any industry where temperature control is critical, this system helps maintain kiln safety and efficiency without added complexity.